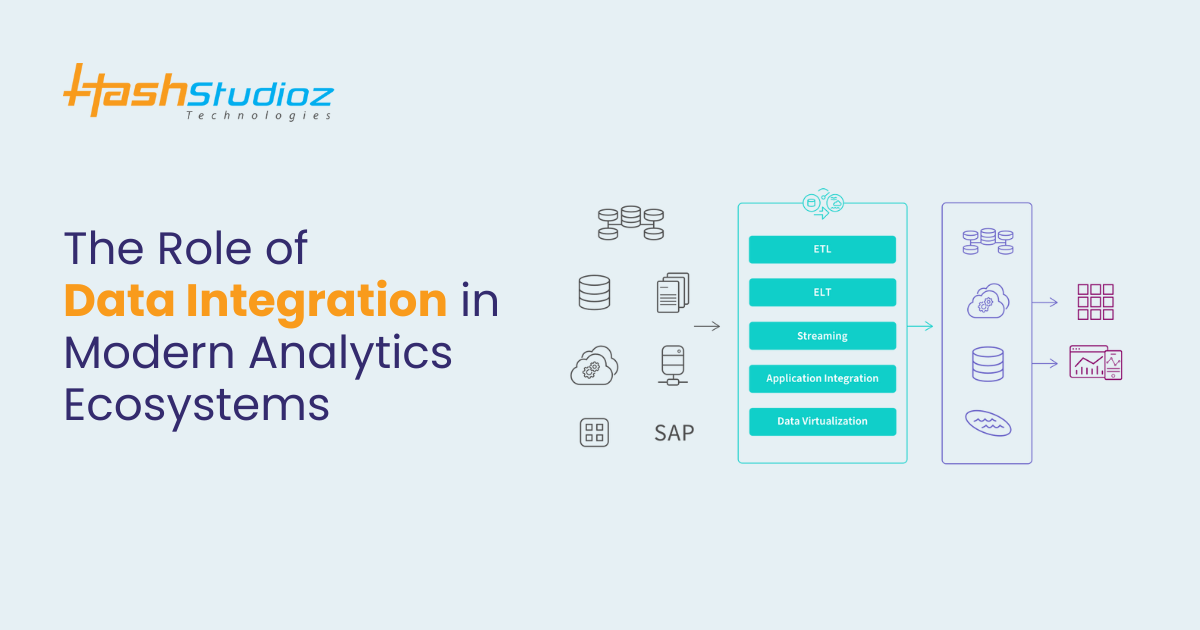
Data has become the lifeblood of modern businesses, driving insights, decision-making, and competitive advantages. In today’s data-driven world, organizations handle vast amounts of data from multiple sources. However, extracting actionable insights from this data requires seamless integration. This is where data integration plays a pivotal role in creating modern analytics ecosystems. By enabling unified access to data, organizations can harness its true potential to enhance business outcomes.
This article delves into the nuances of data integration, its critical role in analytics ecosystems, and strategies for its effective implementation. Additionally, it highlights the importance of working with experts, such as those provided by Data Analytics Services companies, to overcome integration challenges.
- 90% of businesses cite data integration as a critical success factor for analytics.
- Companies leveraging integrated data experience **40% faster decision-making.
- By 2026, the global data integration market is projected to reach $20 billion, growing at a CAGR of 11%.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Data Integration
- Components of a Modern Analytics Ecosystem
- The Key Role of Data Integration in Modern Analytics
- Strategies for Effective Data Integration
- Challenges in Data Integration
- The Role of Professionals in Data Integration
- Benefits of Data Integration in Analytics
- How Data Analytics Services Companies Drive Integration Success
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Understanding Data Integration
What is Data Integration?
Data integration is the process of combining data from multiple, often disparate sources into a unified view. This process typically involves collecting, transforming, and consolidating data to ensure it is accessible and actionable. Integrated data is usually stored in a centralized repository, such as a data warehouse or data lake, where it can be analyzed efficiently and used for informed decision-making.
Importance in Analytics Ecosystems
In the context of modern analytics ecosystems, data integration serves as the foundation for extracting meaningful insights. Without a cohesive integration strategy, organizations risk dealing with fragmented information, inefficiencies, and missed business opportunities.
Key benefits of data integration include:
- Improved Data Accessibility: Ensures data from all sources is readily available for analysis.
- Enhanced Data Quality: Eliminates redundancies, inconsistencies, and errors, ensuring clean and reliable data.
- Streamlined Analytics Processes: Reduces the time and effort required to prepare data, enabling faster insights.
Types of Data Integration
- Manual Data Integration
- Relies on human effort to gather and combine data from various sources.
- Suitable for small datasets or ad-hoc integration needs but not scalable for large or complex datasets.
- Middleware Data Integration
- Uses middleware software to act as a bridge between different systems and enable seamless data flow.
- Common in businesses with diverse systems that need real-time or near-real-time data exchange.
- Application-Based Integration
- Directly integrates data through applications designed to connect specific systems.
- Ideal for integrating enterprise tools like CRM or ERP systems.
- Cloud-Based Integration
- Leverages cloud platforms to centralize data from various on-premise and cloud-based sources.
- Provides scalability, flexibility, and remote accessibility, making it a popular choice for modern businesses.
Components of a Modern Analytics Ecosystem
To fully grasp the significance of data integration, it is crucial to understand the foundational components that make up a modern analytics ecosystem. These components work in tandem to enable data-driven decision-making and business insights.
1. Data Sources
Data sources serve as the origin points of information within an analytics ecosystem. They encompass a variety of systems and platforms that generate or store data.
Types of Data Sources:
- Transactional Systems:
- Examples: ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), CRM (Customer Relationship Management), and POS (Point of Sale) systems.
- Role: Capture day-to-day business operations, including sales, customer interactions, and inventory management.
- External Sources:
- Examples: Social media platforms, IoT (Internet of Things) devices, and APIs (Application Programming Interfaces).
- Role: Provide additional context and real-time data, such as customer sentiment, environmental conditions, or third-party integrations.
- Legacy Systems:
- Examples: On-premise databases and outdated IT infrastructure.
- Role: Store historical data critical for trend analysis and decision-making.
2. Data Warehouses and Data Lakes
Data warehouses and lakes form the core storage systems within an analytics ecosystem, designed to store and manage vast amounts of data for further processing and analysis.
- Data Warehouses:
- Definition: Structured repositories optimized for querying and analysis.
- Use Case: Ideal for operational reporting and structured data analysis, such as financial reports or KPIs (Key Performance Indicators).
- Examples: Snowflake, Amazon Redshift.
- Data Lakes:
- Definition: Flexible repositories designed to store raw, semi-structured, or unstructured data.
- Use Case: Suited for exploratory analysis, big data processing, and machine learning model training.
- Examples: AWS S3, Azure Data Lake.
3. Analytics Tools
Analytics tools are the engines of insight generation in an analytics ecosystem. They process data from warehouses and lakes to deliver actionable intelligence.
Categories of Analytics Tools:
- Business Intelligence (BI) Tools:
- Purpose: Simplify data visualization, reporting, and dashboard creation.
- Examples: Power BI, Tableau, QlikView.
- Benefits: Enable non-technical users to explore and interpret data easily.
- AI and Machine Learning Platforms:
- Purpose: Use advanced algorithms for predictive and prescriptive analytics.
- Examples: TensorFlow, PyTorch, Scikit-learn.
- Benefits: Enable businesses to uncover hidden patterns and forecast future trends.
Why Data Integration is Essential in this Ecosystem
The integration of data across these components ensures that:
- Data from diverse sources is consolidated.
- Storage systems are populated with accurate and consistent data.
- Analytics tools operate with high-quality, reliable data.
By uniting these components through data integration, organizations can create a cohesive and efficient analytics ecosystem capable of delivering actionable insights and competitive advantages.
The Key Role of Data Integration in Modern Analytics
Data integration is a critical enabler for modern analytics ecosystems, helping organizations to effectively utilize their data assets. It bridges the gap between disparate data sources and creates a seamless flow of information that fuels analytics processes. Below are the key roles data integration plays in modern analytics:
1. Enabling Unified Data Views
One of the primary roles of data integration is to create a unified view of organizational data. This comprehensive perspective is essential for businesses to derive meaningful insights and foster collaboration.
Benefits of Unified Data Views:
- Eliminating Data Silos: By breaking down barriers between isolated systems, data integration ensures that all departments have access to the same reliable information.
- Enabling Cross-Functional Insights: Integrated data supports cross-departmental analytics, helping teams collaborate on insights that benefit the organization as a whole.
- Providing a 360-Degree View: With a complete view of customers, operations, and market trends, businesses can make more informed and strategic decisions.
2. Enhancing Decision-Making with Real-Time Insights
In a fast-paced business environment, the ability to analyze data in real-time is a significant competitive advantage. Data integration facilitates this by enabling real-time data flows.
How Real-Time Insights Drive Decisions:
- Responding Promptly to Market Changes: Businesses can adapt to market dynamics, such as demand spikes or competitive actions, without delay.
- Enhancing Operational Efficiency: Real-time monitoring allows organizations to identify inefficiencies and take corrective actions immediately.
- Supporting Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics: Integrated real-time data feeds predictive and prescriptive models, enabling businesses to anticipate future outcomes and recommend actionable strategies.
3. Simplifying Data Governance and Compliance
With growing regulatory requirements and the increasing importance of data security, data integration plays a pivotal role in ensuring compliance and governance.
Advantages of Integration in Governance and Compliance:
- Maintaining Consistent Data Policies: Integrated data systems simplify the enforcement of standardized data governance practices across the organization.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: By centralizing and organizing data, organizations can more easily meet the requirements of regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act).
- Reducing Risks Associated with Data Breaches: An integrated approach to data management enables better monitoring and control, minimizing the chances of unauthorized access or leaks.
Strategies for Effective Data Integration
Developing a robust data integration strategy is essential for organizations to maximize the value of their data. By implementing the right approaches, businesses can streamline their analytics processes and ensure high-quality, actionable insights. Below are key strategies for effective data integration:
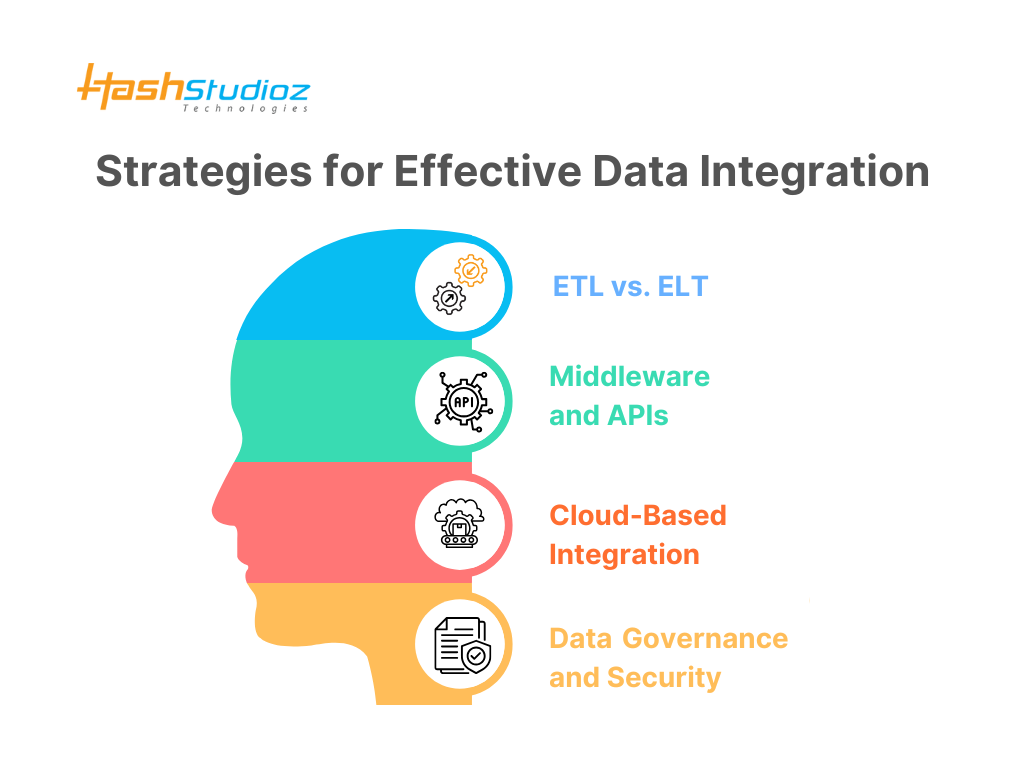
1. ETL vs. ELT
Understanding and selecting the appropriate data preparation method—ETL or ELT—can significantly impact the efficiency of your integration processes.
- ETL (Extract, Transform, Load):
- Process: Data is extracted from source systems, transformed into the desired format, and then loaded into the target system.
- Best For: Traditional data warehouses where data needs to be structured and cleansed before loading.
- Advantages: Ensures high data quality and compliance with predefined schemas.
- Limitations: Slower when dealing with massive datasets or unstructured data.
- ELT (Extract, Load, Transform):
- Process: Data is extracted from source systems, loaded into the target system, and transformed afterward.
- Best For: Modern data lakes and cloud environments where raw data can be stored cost-effectively and processed as needed.
- Advantages: Faster and more scalable for large, complex datasets.
- Limitations: Requires advanced tools and may need additional governance to manage raw data.
2. Middleware and APIs
Middleware solutions and APIs play a crucial role in enabling seamless communication between diverse systems.
- Middleware Solutions:
- Act as intermediaries, allowing disparate systems to connect and exchange data effortlessly.
- Examples: MuleSoft, IBM App Connect, Oracle Integration Cloud.
- Benefits: Simplify complex integrations and support real-time data exchange.
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces):
- Allow direct connectivity between systems by defining clear communication protocols.
- Benefits: Highly flexible and enable integration with external data sources, such as social media platforms or IoT devices.
3. Cloud-Based Integration
Cloud platforms have revolutionized data integration by offering scalable and cost-effective solutions.
- Platforms: Popular options include AWS (Amazon Web Services), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
- Benefits of Cloud Integration:
- Scalability: Easily handle growing data volumes and evolving business needs.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Pay-as-you-go models reduce the financial burden of on-premise infrastructure.
- Flexibility: Integrate data from on-premise systems, cloud applications, and external sources seamlessly.
- Real-Time Processing: Leverage cloud-native tools for real-time data integration and analytics.
4. Data Governance and Security
Data governance and security are critical components of any data integration strategy.
- Governance Practices:
- Establish clear policies for data ownership, usage, and quality.
- Implement metadata management to provide transparency into data sources and transformations.
- Security Measures:
- Encryption: Protect data at rest and in transit.
- Access Controls: Restrict data access to authorized personnel.
- Compliance: Ensure adherence to regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA.
- Monitoring: Use tools to detect and address anomalies or potential breaches in real-time.
Challenges in Data Integration
Despite its critical role in modern analytics ecosystems, data integration comes with its own set of challenges. These hurdles often arise due to the complexity of combining data from disparate systems while ensuring accuracy, consistency, and scalability. Below are some of the key challenges organizations face during data integration:
1. Handling Diverse Data Sources
Modern businesses rely on data from multiple systems, each with its own format, protocol, and structure.
Key Issues:
- Variety in Data Formats: Data may come in structured (databases), semi-structured (JSON, XML), or unstructured (text, videos) formats, making integration complex.
- Inconsistent Protocols: Different systems might use incompatible protocols or APIs for data exchange.
- Legacy Systems: Older systems may lack modern integration capabilities, creating additional hurdles.
Potential Solutions:
- Use middleware and API connectors to bridge gaps between incompatible systems.
- Standardize data formats and protocols wherever possible to simplify integration workflows.
2. Ensuring Data Quality
The accuracy and reliability of integrated data directly impact the quality of analytics outcomes.
Key Issues:
- Duplicate Records: Multiple systems may store overlapping data, leading to redundancies.
- Incomplete or Missing Data: Essential data points may be absent or not properly captured.
- Inconsistent Data Values: Different systems may store similar data in varied formats (e.g., “Jan” vs. “January”).
Potential Solutions:
- Implement robust data cleansing processes to remove duplicates, fill missing values, and standardize formats.
- Use automated validation tools to detect and correct data inconsistencies.
- Monitor data quality metrics regularly to maintain high standards.
3. Balancing Performance and Scalability
As data volumes grow exponentially, maintaining integration performance without compromising scalability is a continuous challenge.
Key Issues:
- Performance Bottlenecks: Complex transformations or large data volumes can slow down integration processes.
- Scalability Constraints: Traditional on-premise systems may struggle to handle expanding datasets.
- Real-Time Processing Needs: The demand for real-time analytics places additional pressure on integration pipelines.
Potential Solutions:
- Leverage cloud-based integration platforms that offer elastic scalability.
- Optimize ETL/ELT processes to handle large volumes efficiently.
- Use distributed processing frameworks like Apache Spark to manage high data throughput.
The Role of Professionals in Data Integration
The success of any data integration initiative often hinges on the expertise and contributions of skilled professionals. Their ability to manage complex processes, ensure data quality, and align integration with business goals makes them indispensable in modern analytics ecosystems. Below is an in-depth exploration of their roles and contributions.
Why Hire Data Analysts?
Data analysts play a pivotal role in ensuring that integrated data becomes actionable intelligence. Their technical and analytical expertise transforms raw data into valuable insights.
Key Benefits of Hiring Data Analysts:
- Expertise in Data Modeling and Transformation:
- Data analysts design effective data models to organize and structure data for integration.
- They apply advanced transformation techniques to cleanse and standardize data.
- Accurate Interpretation of Analytics Results:
- With their analytical skills, data analysts can identify trends, correlations, and anomalies in integrated datasets.
- Their interpretations provide actionable insights for decision-making.
- Seamless Integration and Visualization of Data:
- Data analysts use tools like Tableau, Power BI, and SQL to ensure smooth integration and create intuitive dashboards.
- They make complex data accessible and understandable for stakeholders.
Contributions of a Data Analytics Services Company
Specialized data analytics services companies bring end-to-end solutions and deep expertise to the table, making them invaluable for large-scale or complex integration projects.
Key Contributions:
- Custom Integration Solutions:
- Tailored to align with unique business requirements, these solutions address specific challenges such as handling diverse data sources or real-time integration.
- Advanced Analytics Capabilities:
- Leveraging cutting-edge technologies like AI and machine learning, these companies enhance the analytical power of integrated datasets.
- Scalability and Long-Term Sustainability:
- They design integration architectures that are future-proof, ensuring smooth scalability as data volumes and analytics demands grow.
- Ongoing support ensures systems remain efficient and compliant over time.
Tailored Data Analytics Solutions
Organizations benefit greatly from data analytics solutions that are customized to their objectives and challenges. These solutions ensure maximum ROI and drive meaningful outcomes.
Key Advantages of Tailored Solutions:
- Alignment with Business Goals: Customized solutions address specific pain points, whether it’s improving customer insights, optimizing operations, or enhancing compliance.
- Maximized Efficiency: Tailored approaches streamline workflows and eliminate redundancies.
- Improved Decision-Making: Solutions designed around the organization’s data landscape deliver insights that directly support strategic goals.
Benefits of Data Integration in Analytics
Data integration is a cornerstone of modern analytics, providing numerous advantages that empower organizations to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and prepare for future growth. Below are the key benefits of data integration in analytics, explained in detail:
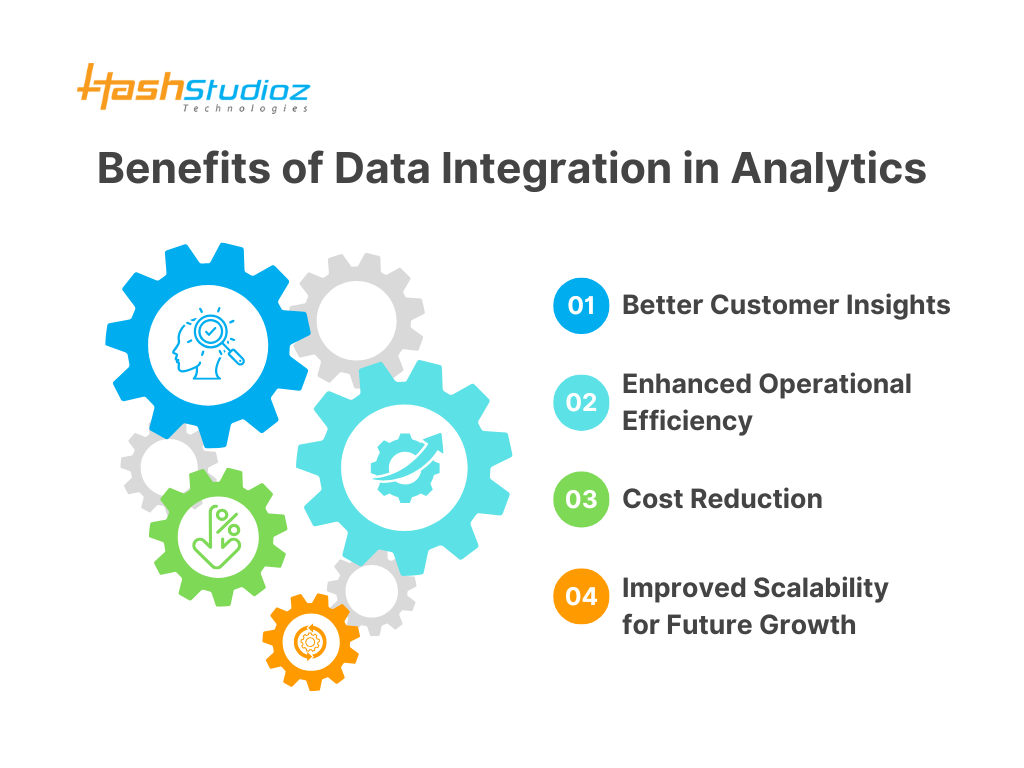
1. Better Customer Insights
Integrated data provides a 360-degree view of customer behavior by consolidating data from various touchpoints, such as CRM systems, social media platforms, and transactional databases.
Key Benefits:
- Personalized Strategies: By understanding customer preferences and behaviors, organizations can tailor marketing campaigns, offers, and customer service experiences to individual needs.
- Improved Retention Rates: Insights into customer pain points and satisfaction levels allow businesses to address concerns proactively, reducing churn.
- Enhanced Customer Segmentation: Integrated data supports precise segmentation, enabling more effective targeting and engagement strategies.
2. Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Streamlined processes and centralized data management improve the overall efficiency of an organization’s operations.
Key Benefits:
- Reduced Manual Effort: Automated data integration eliminates the need for time-consuming manual data collection and consolidation.
- Improved Collaboration: A unified data repository ensures that all departments work with the same reliable data, fostering better communication and teamwork.
- Faster Decision-Making: With all relevant data readily available, businesses can respond swiftly to operational challenges and market opportunities.
3. Cost Reduction
Data integration helps organizations reduce costs by eliminating inefficiencies and redundancies while enabling better resource utilization.
Key Benefits:
- Automation Savings: Automating data flows reduces the costs associated with manual labor and repetitive tasks.
- Eliminating Redundancies: Integrated systems prevent duplicate data storage and processing, saving storage and processing costs.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Accurate and timely insights allow organizations to allocate resources effectively, minimizing waste and maximizing ROI.
4. Improved Scalability for Future Growth
Integrated systems are designed to grow alongside the organization, ensuring they remain relevant and effective as data volumes and business needs expand.
Key Benefits:
- Adaptability: Integrated platforms can incorporate new data sources and systems without disrupting existing workflows.
- Future-Proofing: Scalability ensures that the organization is prepared for increased data demands, whether due to business expansion or new analytics requirements.
- Support for Advanced Analytics: Integrated systems provide a solid foundation for adopting advanced technologies like AI, machine learning, and predictive analytics.
How Data Analytics Services Companies Drive Integration Success
Data integration can be a complex process, but with the expertise and tools provided by data analytics services companies, organizations can achieve seamless integration and unlock the full potential of their data. These companies play a pivotal role in ensuring that integration efforts are not only successful but also aligned with business goals. Below are the ways in which these companies drive integration success:
1. Role of Data Analysts
Hiring skilled data analysts through a data analytics services company brings invaluable expertise to the integration process.
Key Contributions of Data Analysts:
- Interpreting Integrated Data: Data analysts transform raw, integrated data into actionable insights, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Data Modeling: They design robust models to ensure that integrated data is structured optimally for analysis.
- Ensuring Data Quality: Analysts validate and cleanse data to maintain accuracy, consistency, and reliability.
- Visualization Expertise: Using tools like Tableau and Power BI, they create dashboards that simplify the representation of complex integrated data for stakeholders.
2. Tools and Technologies Used
Data analytics services companies rely on cutting-edge tools and platforms to facilitate efficient and scalable data integration.
Popular Tools and Technologies:
- Hadoop and Apache Spark: These big data platforms handle massive datasets and enable distributed processing, ensuring performance and scalability.
- Tableau and Power BI: These visualization tools help convert integrated data into user-friendly dashboards and reports.
- ETL Platforms: Tools like Talend, Informatica, and Alteryx are used to extract, transform, and load data efficiently.
- Cloud Platforms: AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud offer scalable and flexible infrastructure for integration and analytics.
Impact of Advanced Tools:
- Streamlined Workflows: Automation and advanced processing capabilities reduce manual effort and errors.
- Real-Time Processing: Tools like Apache Kafka enable real-time data integration, supporting real-time analytics needs.
- Future-Proofing: Technologies like AI and machine learning are embedded into these tools to prepare organizations for advanced analytics.
3. Custom Data Analytics Solutions
No two organizations are alike, and a one-size-fits-all approach rarely works for data integration. This is where tailored data analytics solutions come into play.
How Tailored Solutions Drive Success:
- Alignment with Business Goals: Custom solutions address specific challenges, whether it’s managing diverse data sources, real-time integration, or compliance requirements.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Tailored systems grow with the organization, ensuring long-term relevance and adaptability.
- Maximized ROI: By focusing on the unique needs of a business, these solutions ensure efficient resource utilization and better outcomes.

Conclusion
Data integration is a cornerstone of modern analytics ecosystems. It transforms fragmented datasets into unified, actionable insights, driving operational excellence and strategic decision-making. By partnering with a reliable Data Analytics Services company, businesses can overcome integration challenges, adopt tailored solutions, and unlock the full potential of their data.
Whether it’s about improving data accessibility, ensuring compliance, or enhancing decision-making, effective data integration is indispensable. Organizations looking to stay competitive should hire data analysts and invest in robust Data Analytics Solutions to thrive in the digital era.
FAQs
1. What is data integration, and why is it important?
Data integration is the process of combining data from different sources into a unified view. It is crucial for eliminating silos, improving data quality, and enabling comprehensive analytics.
2. How does data integration support compliance?
Integrated data ensures consistent application of governance policies and simplifies reporting for regulatory compliance.
3. Why should I hire data analysts for my business?
Data analysts bring expertise in managing, interpreting, and visualizing data, ensuring that integration efforts align with business goals.
4. What are the challenges of data integration?
Common challenges include handling diverse data sources, ensuring data quality, and balancing scalability with performance.
5. How do Data Analytics Services companies help?
These companies provide tailored solutions, advanced analytics tools, and expertise to streamline data integration and analytics processes.