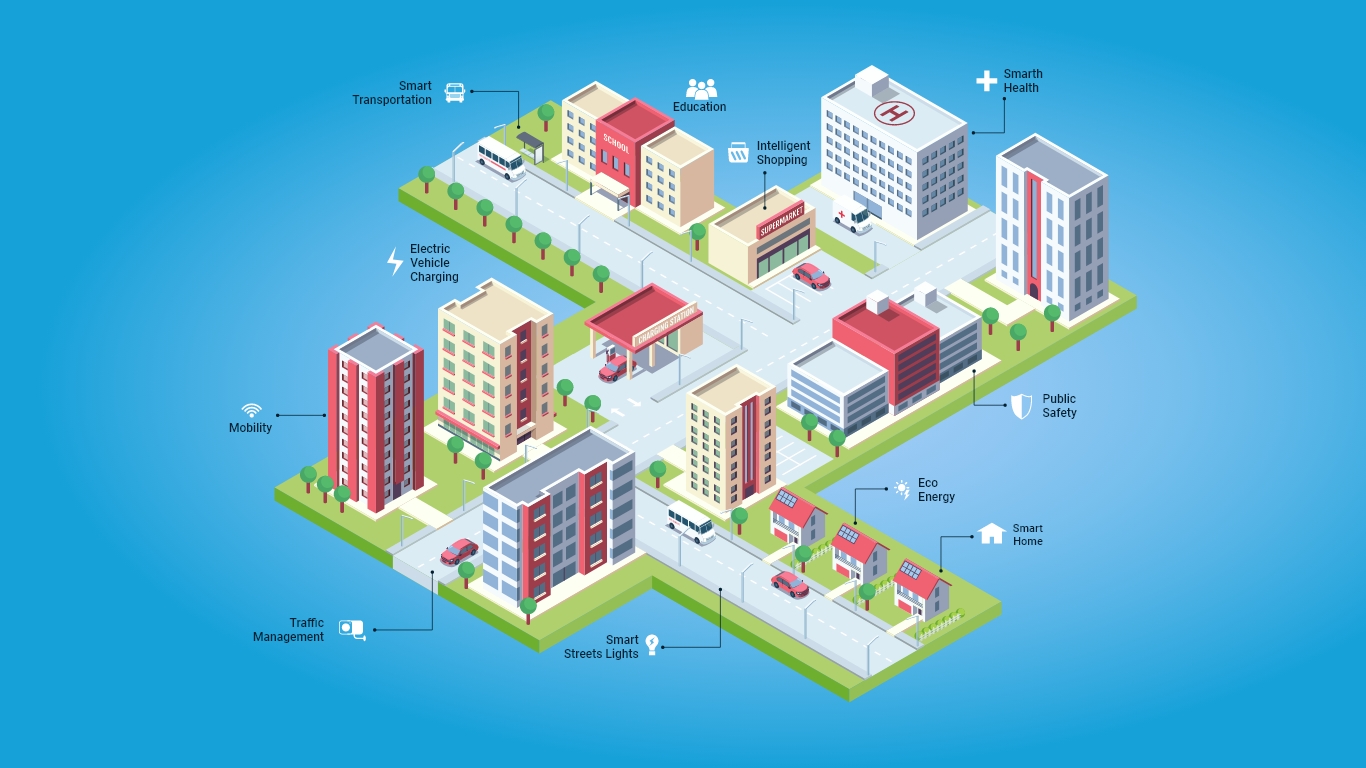
The smart city idea can be interpreted as a structure for bringing into motion a vision of advanced and modern urbanization. Smart cities make use of technology to create an atmosphere that is conducive to business investment while also helping governments to optimize resource use and accountability.
- A study by the World Economic Forum found that blockchain could save cities up to $10 billion per year by 2025.
- A survey by PwC found that 66% of city governments are considering using blockchain technology.
- A report by Gartner predicts that by 2025, 20% of all smart city projects will use blockchain.
- The top five countries in terms of blockchain adoption for smart cities are China, the United States, the United Arab Emirates, Singapore, and Estonia.
- The market is expected to grow to $23.3 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 42.2%.
- The biggest challenges to the adoption of blockchain in smart cities are security, scalability, and interoperability.
One popular example of an intelligent metropolitan ecosystem is smart lighting. Through remote access, we can precisely adjust and dim lights as needed, saving energy, optimizing costs, improving service quality, and raising citizen satisfaction.
Table of Contents
Smart City and Its Impact on the Environment

Smart-city technologies including air quality control, energy usage management, and power, water, and waste tracking will lead to reductions in GHG pollution of 10-15%, 30-130 kilograms of solid waste per person per year, and 25-80 liters of water saved per person per day. The most common use cases for blockchain in smart cities are identity management, asset tracking, data sharing, and smart contracts.
Here are some of the ways that blockchain can be used in a smart city ecosystem:
- Health – Blockchain technology has the potential to endanger public health by building a stable and scalable ecosystem for exchanging electronic health records (EHRs). In Singapore, blockchain is being used to develop a smart healthcare system. This system is helping to improve the efficiency and security of patient records and medical data.
- Education – By allowing trustworthy provenance and traceability from farmer to customer, blockchain technology can be used to improve transparency, reduce uncertainty, and lower costs in food-based supply chains. Agriculture insurance and the use of blockchain technologies to document and maintain agricultural land records are two other potential uses.
- Land- Blockchain technology can be used to increase transparency and reduce complexity and cost in food-based value chains by enabling trustworthy provenance and traceability from farmer to consumer.
- Intelligent government services – Blockchain technology can be used to crack the silos, check government corruption, and improve productivity and accountability. Using a blockchain to link files and data transfer between agencies will enhance accountability and ensure that the data/file goes forward in real-time.
- Energy and waste management- A database of generated and used energy for each grid user can be stored on a blockchain using smart meters, with credits/currency assigned to the user for surplus power supply and credits repaid for power usage. This ultimately results in a demand for electricity that is transparent, hassle-free, and efficient.
- Public safety – By addressing the issue of interagency communication by creating a unified basis of reality that each agency individually interfaces with depending on predefined requirements, blockchain could allow public safety distribution more effectively.
- Citizen participation- Blockchain will help make citizen documents more tamper-proof, resilient, safe, and private, helping a wide range of stakeholders.
Use Cases of Blockchain in Smart City
Since blockchain-based smart cities are only in their early stages of growth, blockchain analysts and regular people around the world speculate about their future usage cases, which have a fair chance of being a reality eventually.
Dubai stands out among cities with urban blockchain-based ventures, with a $300 million investment aiming to make it the world’s first city to implement blockchain into all of its facilities by 2020.
Here are a few examples of how this technology is being used in Smart city planning:
- Security- Blockchain enhances the security of physical and personal information collected through the Internet. Some examples include smart locks and digital security systems.
- Energy- Smart blockchain-based contracts, solar-powered households can now seamlessly share surplus electricity with other grid participants.
- Mobility- The e-vehicle and e-mobility sectors would broaden, allowing consumers to access more accessible and environmentally friendly mobility alternatives.
- Waste- Blockchain will offer real-time container information to the general public and waste disposal systems.
- Participation- Blockchain technology is utilized to provide reliable, transparent, accountable, and private-public consultations in elections, surveys, and referendums.
Advantages Brought Up By Smart Cities
Smart cities are characterized as cities that can use information technology to enhance efficiencies, sustainability, and the quality of life of their inhabitants. The most important benefits of blockchain for the city administration, according to Blockchain for Cities experts, are:
- Increased transparency and connectivity: Cities will use blockchain vertical utilities like accessibility, power, and security to connect with their people in real time through a single open, accessible, transversal process.
- Direct communication- Blockchain helps government agencies and the general public to communicate digitally. For example, bureaucratic processes at registries, town halls, and other government departments will be sped up.
- Integrity over information- With this Blockchain, it is possible to absolutely or partially encrypt a file in order to share only the parts of it that are of interest, privately, anonymously, and without the risk of a third party manipulating it.
- Efficient management- Thanks to blockchain, the public and community officials will be able to see where each resource comes from and where it is actually going. In addition, without jeopardizing people’s anonymity, they would be able to see how public services are used.
- Infrastructure improvement:– Cities will use smart technologies to produce predictive analytical reports that identify problems that need to be resolved before an infrastructure breakdown happens.
If you have questions or would like more information about smart cities, please visit our blockchain development Services page. You can also send an email to info@localhost.
FAQs
What are some specific examples of how blockchain is being used in smart city ecosystems today?
There are a number of specific examples of how blockchain is being used in smart city ecosystems today. Here are a few examples:
- Energy management: The city of Zug, Switzerland is using blockchain to track the energy consumption of its citizens and businesses. This data is used to improve energy efficiency and reduce costs.
- Public transportation: The city of Seoul, South Korea is using blockchain to track the movement of public transportation vehicles. This data is used to improve efficiency and reduce congestion.
- Waste management: The city of San Francisco is using blockchain to track the movement of waste. This data is used to improve efficiency and reduce pollution.
- Land registry: The government of Honduras is using blockchain to create a secure and transparent land registry. This has helped to reduce fraud and improve property rights.
- Supply chain management: The company Walmart is using blockchain to track the movement of food products. This data is used to ensure food safety and traceability.
What are the potential risks of using blockchain in a smart city ecosystem?
There are a number of potential risks associated with using blockchain in a smart city ecosystem. Here are a few examples:
- Security: Blockchain is a secure technology, but it is not immune to attack. If a hacker were to gain access to the blockchain, they could potentially steal data or disrupt the network.
- Complexity: Blockchain is a complex technology, and it can be difficult to implement and manage. This can lead to errors and security vulnerabilities.
- Regulation: The regulatory landscape for blockchain is still evolving, and it is not clear how blockchain-based applications will be regulated in the future. This could lead to uncertainty and compliance risks.
What are the ethical implications of using blockchain in a smart city ecosystem?
The use of blockchain in a smart city ecosystem raises a number of ethical implications. Here are a few examples:
- Privacy: Because blockchain technology is transparent, every transaction is visible to everyone as it is recorded there. This could raise privacy concerns for citizens and businesses.
- Data ownership: Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology, which means that data is stored on multiple nodes. This raises questions about who owns the data and how it can be used.
- Algorithmic bias: Blockchain-based applications often use algorithms to make decisions. This could lead to algorithmic bias, which could disproportionately impact certain groups of people.
What are the challenges of using blockchain technology in a smart city ecosystem?
The challenges of using blockchain technology in a smart city ecosystem include:
- Cost: Blockchain is a relatively new technology, and the cost of implementing it can be high.
- Complexity: Blockchain is a complex technology, and it can be difficult to implement and manage.
- Regulation: The regulatory landscape for blockchain is still evolving, and it can be difficult to comply with all applicable regulations.
It is important to carefully consider the ethical implications of using blockchain in a smart city ecosystem before implementing any blockchain-based applications.