Connectivity is one of the most important aspects of the Internet of Things ecosystem. Thousands of IoT devices are interconnected using numerous protocols and methods. An M2M SIM cards are one of the most efficient methods for building a large network of connected devices.
- The global M2M SIM card market is expected to reach $100 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 15.3% from 2023 to 2025.
- The manufacturing and logistics sectors are the two largest end-user markets for M2M SIM cards, accounting for 35% and 25% of the market share, respectively.
- The automotive sector is the fastest-growing end-user market for M2M SIM cards, with a CAGR of 20% from 2023 to 2025.
- The number of connected devices using M2M SIM cards is expected to reach 14.2 billion by 2025.
- The most popular M2M SIM card technology is 2G, followed by 3G and 4G.
Although machine-to-machine connectivity has been around for decades, the Internet of Things (IoT) is getting more attention these days. Despite the different terminology, the concept is the same: connected machines (or things) communicate with one another. And M2M SIM cards enable this type of communication.
Find out more about M2M SIMs, their differences from traditional SIMs, and why they are so crucial for IoT deployments.
Table of Contents
What are M2M SIM Cards?
M2M (machine-to-machine) refers to technology that enables devices to communicate with each other and perform actions without requiring human intervention. An M2M SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) is a small computer chip that allows an M2M device to connect to cellular networks and other devices.
How do M2M SIMs Differ from Traditional SIMs?
M2M SIMs look exactly like traditional SIM cards. The two have many similarities and multiple form factors, but they differ in more ways than they are similar.
- More Memory: The large amount of data that is sent and received by M2M SIMs makes them capable of storing greater amounts of data than traditional SIMs.
- Global Roaming: IoT systems that cross country borders often need to send and receive data to and from hubs in other countries. An M2M SIM card can connect to multiple operators in multiple countries with a single package and standardized tariffs.
- Longevity: M2M SIMs are often used in long-term projects where the device is not easily accessible. For example, on a farm, on an ocean cargo ship, or underground. Due to this, M2M SIM cards can last up to 10 years.
- Durability: M2M SIM cards can withstand harsh conditions such as extreme heat or cold. Some SIM cards can operate at temperatures as low as –40°F and 221°F. Embedded M2M SIMs are also corrosion- and vibration-resistant. No matter what kind of equipment they’re in, such as underground mining equipment or agricultural soil sensors in cornfields, their work will continue.
- Increased Security: M2M SIM cards utilize various technologies to increase IoT security, such as APNs and private access points to separate their data flow from the rest of an operator’s data traffic.
How does M2M Work?
A primary function of M2M technology is to extract sensor data and transmit it over the network. An M2M system typically uses cellular or Ethernet networks and consists of three main components:
- Data endpoint (DEP): The data to be monitored or transmitted is contained within this system. A data endpoint is a microcomputer system that consists of transmitters and receivers. Many devices and data endpoints are connected to the network.
- Communication networks: Data is transferred between machines using cellular networks and wireless or wired internet connections.
- Data integration point (DIP): This machine receives information. A network can have multiple data endpoints, but only one data integration point. The DIP can be a control center for meter readings, a server, or a web crawler.
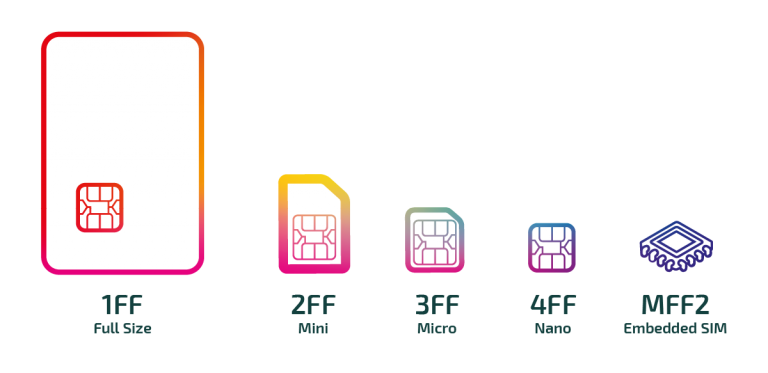
M2M SIM Form Factors
M2M SIMs are available in every form factor, so it is easy to find one that fits your device design & the size and features you require.
- Mini SIM (2FF): Mini SIMs are currently the largest removable SIM cards. Since the mid-1990s, this SIM has been in use. As of today, the Mini SIM has remained a great option for devices connected to the internet, such as cars and vending machines.
- Micro SIM (3FF): A Micro SIM has a significantly smaller size than a Mini-SIM. It is large enough to facilitate physical SIM card swaps. Tablets and telehealth monitors are better suited for mid-sized IoT devices.
- Nano SIM (4FF): Nano SIMs are smaller and slimmer than the Mini and Micro SIMs. They are ideal for compact IoT devices, such as wearables. When a human is installing the device, the removable form factors 2FF, 3FF, and 4FF are good choices. The purpose of this is to assist with the initial booting of the device and SIM provisioning.
- Embedded SIM (MFF2): Embedded SIMs (or eSIMs) provide better durability since the SIM is protected within the device. The latest MFF2 SIM cards often support eUICC remote provisioning. For many IoT deployments, especially those in rural areas or involving vehicles in motion, remote provisioning is beneficial. As an example, eUICC allows scooters to move from one city to another without requiring new SIM cards.
M2M SIM Card Use Cases
A wide range of industries use M2M SIM cards, including retail, smart homes, agriculture, healthcare, and smart grid applications. Here are a few examples of how they can be used in particular fields.
Healthcare
- Wearables: M2M SIM cards are used in wearables to track patients’ health wherever they are. People with chronic diseases such as diabetes will especially benefit from this. Devices with M2M SIM cards are able to monitor vitals without connecting to Wi-Fi.
- Health Monitors: M2M SIM cards ensure that physicians and doctors receive patient health data consistently and at any time. In critical situations, every second counts.
Manufacturing
- Robots: M2M SIM cards can be integrated into robots to connect them globally within a single network across various manufacturing sites. Instead of relying on the internet, this will allow connection even in remote locations.
- Predictive Equipment Maintenance: Manufacturers can fix equipment issues more easily and cheaply before they cause problems. Downtime causes losses of hundreds of thousands of dollars per second, so monitoring all systems and mechanisms is crucial. M2M SIM cards can be embedded in sensors attached to equipment to alert staff when work speed or efficiency changes. The Internet of Things (IoT) can also help track staff hours and remind them to get regular checkups.

Retail
- Cashierless Checkout: Having no lines to wait in and no cashiers to serve you sounds great. Amazon is the first company to introduce this concept with its Amazon Go stores, where you can walk out with your purchases and the system will automatically charge your credit card. A smart shelf with product tracking and a smart camera with facial recognition make this magic happen.
- Inventory and Product Management: Retailers can use various trackers to track their products across multiple warehouses, predict demand, and evaluate the condition of the goods. This helps manage products, order more when needed, and move products between stores and warehouses efficiently.
Agriculture
- Predictive Agriculture: Agricultural facilities are often miles apart, so it’s crucial to keep all devices connected in areas that don’t have fast internet access. Using M2M SIM cards, farmers can connect all sensors together. With smart AI data processing, they can determine the most suitable period for harvesting, planting, and irrigation.
- Drones and Robots: A drone that spreads pesticides across miles and fields can always remain connected to a cellular network. Also, robots can assist in the harvest, seeding, watering, and detection of plant diseases.
Logistics
- Predictive Delivery: The logistics network is usually too broad to rely solely on Internet connections to deliver goods by air, sea, and land. Trackers powered by M2M SIM cards can help businesses track transport, manage routes, and predict delivery times.
- Inventory and Supply Management: An M2M SIM card can help warehouses track assets, products, and goods and calculate current and historical supply vs. demand.
Is M2M SIM Card Beneficial for Your Business?
Whether or not an M2M SIM card is beneficial for your business depends on your specific needs. However, there are a number of potential benefits that M2M SIM cards can offer businesses, including:
- Increase customer satisfaction: By using M2M SIM cards to provide remote monitoring and control of devices, businesses can improve customer satisfaction by ensuring that their products and services are always up and running.
- Reduce costs: By using M2M SIM cards to collect data and automate processes, businesses can reduce costs by eliminating the need for manual labor.
- Improve compliance: By using M2M SIM cards to track assets and monitor devices, businesses can improve compliance with regulations.
- Remote monitoring and control: M2M SIM cards can be used to remotely monitor and control devices, such as machinery, vehicles, and assets. This can help businesses to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and prevent downtime.
- Data collection and analysis: M2M SIM cards can be used to collect data from devices, such as temperature, humidity, and location data. This data can then be analyzed to improve decision-making and optimize processes.
Connecting the Future of Things with M2M SIMS
M2M SIM cards have revolutionized the way machines communicate, enabling seamless connectivity and unlocking a world of possibilities. With their compact size and robust capabilities, these tiny marvels have found applications in various industries, from transportation and healthcare to agriculture and manufacturing. As we delve deeper into the era of the Internet of Things (IoT), M2M SIM cards will continue to play a pivotal role in connecting devices, collecting data, and optimizing operations. Whether it’s monitoring assets in real-time, automating processes, or enhancing efficiency, the versatility and reliability of M2M SIM cards make them an indispensable component of our interconnected future.