Long-range Bluetooth, also known as Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) with Long-Range Mode, is a feature of Bluetooth 5.0 and newer versions. It allows devices to communicate over extended distances while maintaining low power consumption. This is achieved through the use of Coded PHY (Physical Layer) modes, such as S=2 and S=8, which improve signal sensitivity and extend communication range up to 400 meters or more in open spaces, 4x the range of standard Bluetooth — all while maintaining low power consumption depending on environmental conditions.
Did You Know?
- Over 70% of IoT applications rely on Bluetooth due to its reliability and energy efficiency.
- 60 billion Bluetooth devices will be in use globally by 2026.
- Bluetooth-enabled beacons have driven a 40% increase in foot traffic for retail stores.
Why Settle for Less When You Can Have the Best? Choose HashStudioz for Your IIoT Needs! Contact Us
Table of Contents
How Long-Range Bluetooth Works?
The key to long-range Bluetooth lies in the Coded PHY feature, which adds redundancy to transmitted data, improving the receiver’s ability to decode signals over longer distances. Two coding schemes are commonly used:
- S=2: Doubles the range of standard Bluetooth.
- S=8: Quadruples the range with slower data rates but robust communication.
Bluetooth long-range communication, powered by Coded PHY (Physical Layer), allows Bluetooth devices to extend their communication range significantly—up to 400 meters in open spaces and over 1 kilometer under optimal conditions.
Key Features of Long-Range Bluetooth
- Extended Range: Up to 4x the range of traditional Bluetooth connections.
- Low Power Consumption: Optimized for IoT and battery-operated devices.
- Robust Signal: Better penetration through obstacles like walls, urban areas and other barriers.
- Secure Communication: Includes built-in security protocols for encrypted data transfer.
- Backwards Compatible: Devices can still connect to older Bluetooth versions.
Advantages of Long-Range Bluetooth
- Cost-effective compared to cellular and other long-range communication technologies.
- Highly interoperable across devices and platforms.
- Simple integration with existing systems, leveraging Bluetooth’s widespread adoption.
Examples of BLE-Enabled Devices
- Wearables: Fitness trackers, smartwatches, and health monitors.
- IoT Devices: Smart home sensors, door locks, and thermostats.
- Beacons: Devices for location tracking and proximity marketing.
- Medical Devices: Heart rate monitors, glucose monitors, and other healthcare equipment.
- Industrial Sensors: Devices for predictive maintenance, environmental monitoring, and asset tracking.
Techniques Used in Coded PHY for Long-Range Bluetooth
The Coded Physical Layer (PHY) in Bluetooth communication is designed to improve the robustness and range of signal transmission, particularly in environments with high noise or interference. Several techniques are utilized in Coded PHY to enhance Bluetooth’s performance, especially for long-range communication:
1. Channel Coding
Channel coding refers to the process of adding redundant data to the transmitted signal to allow the receiver to detect and correct errors. This improves the reliability of the communication over longer distances or in noisy environments.
- Forward Error Correction (FEC): One of the most common techniques used in Bluetooth’s Coded PHY. It adds extra bits to the transmitted data, enabling the receiver to detect and correct errors without needing retransmission.
- In Bluetooth 5.0 and later, Reed-Solomon coding and Convolutional Coding are used for error correction. These coding schemes improve the ability of Bluetooth devices to recover from errors, especially over long distances.
- Turbo Codes and LDPC (Low-Density Parity-Check Codes): Advanced error-correcting codes that can provide higher error correction performance while maintaining a reasonable throughput.
2. Modulation Techniques
Modulation is the process of encoding data onto a carrier signal, and the type of modulation significantly impacts the range and reliability of the signal.
- Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK): In Coded PHY, simpler modulation schemes like BPSK can be used. While it reduces the data rate, it significantly enhances the robustness of the signal over long distances.
- Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) and Higher-Order Modulations: Bluetooth 5.0 introduced Coded PHY with QPSK modulation (used in Bluetooth Low Energy for higher throughput). This allows more bits per symbol to be transmitted, but with Coded PHY techniques, the signal becomes more resistant to interference, enabling reliable long-range communication.
3. Coding Gain
Coding gain refers to the improvement in signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) that is achieved by using error-correcting codes. This means that the receiver can correctly decode signals that would otherwise be too noisy to detect. In long-range Bluetooth communication, coding gain is crucial for extending the range without requiring higher transmission power.
- Coded PHY Systems in Bluetooth 5.0: The use of Coded PHY allows the system to effectively extend the range by compensating for signal degradation. Coding schemes like 2M, LE 500 Kbps, and LE 125 Kbps modes use different levels of coding to balance data rate with range.
4. Interleaving
Interleaving is a technique used to rearrange the data in a way that spreads out consecutive bits of data across different transmission symbols. This helps to reduce the impact of burst errors, which can occur due to interference or fading over long distances.
- Block and Convolutional Interleaving: These methods help improve the reliability of Bluetooth transmission by ensuring that errors in one part of the signal do not impact consecutive bits or symbols.
5. Adaptive Coding and Modulation (ACM)
Adaptive coding and modulation enable Bluetooth devices to dynamically adjust the coding and modulation schemes based on the quality of the radio link. When the link quality is high, Bluetooth can switch to higher modulation schemes for higher data rates, while in poor conditions, it can switch to lower modulation schemes with stronger error correction for better range.
- ACM helps in long-range Bluetooth communication by adapting the system to the varying conditions of the wireless channel, thus maximizing the performance without compromising signal integrity.
6. MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) Techniques
Although not commonly used in all Bluetooth implementations, MIMO techniques can be considered for Bluetooth systems designed for very long-range communication. MIMO uses multiple antennas to transmit and receive multiple data streams, increasing the overall data rate and improving signal reliability over longer distances.
Use Cases of Long-Range Bluetooth Communication
1. Industrial IoT (IIoT)
- Asset Tracking: Efficiently monitor and manage assets across large factory floors or extensive warehouse spaces, improving inventory visibility and reducing loss.
- Sensor Networks: Connect multiple sensors for environmental monitoring, predictive maintenance, and machine status updates, enabling real-time decision-making and reducing downtime.
2. Smart Agriculture
- Farm Monitoring: Collect data on soil moisture, temperature, and other environmental factors across expansive fields, improving crop management and yield.
- Irrigation Systems: Automate watering schedules by connecting BLE-enabled irrigation systems, optimizing water usage and reducing waste.
3. Healthcare
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Use BLE-enabled wearable devices to monitor patients’ vitals, ensuring timely interventions and reducing hospital readmissions.
- Hospital Asset Management: Track and manage medical equipment, supplies, and staff across large healthcare facilities, enhancing operational efficiency.
4. Smart Homes and Buildings
- Extended Range for Smart Devices: Improve connectivity for BLE-enabled devices like thermostats, lights, and security systems, even in larger homes or multi-story buildings.
- Building Automation: Control HVAC systems, access control, and energy management over long distances, reducing energy consumption and enhancing convenience.
5. Retail and Proximity Marketing
- Location-Based Services: Use BLE beacons for personalized advertising and customer engagement in stores or shopping centers, driving foot traffic and sales.
- Inventory Management: Track and manage inventory using BLE tags, ensuring stock accuracy and reducing manual checks.
6. Logistics and Supply Chain
- Real-Time Tracking: Monitor goods across warehouses and transit routes, providing live updates and ensuring timely deliveries.
- Environmental Monitoring: Track temperature, humidity, and other conditions during transportation, ensuring product quality (especially for perishables).
7. Sports and Fitness
- Wearable Tracking: Utilize BLE-enabled wearables for real-time performance tracking across large sports fields or during outdoor activities, providing detailed data for athletes and trainers.
8. Smart Cities
- Connected Infrastructure: Link streetlights, traffic signals, and environmental sensors over long distances, improving city management and sustainability.
- Vehicle-to-Infrastructure Communication: Enhance traffic management with real-time data exchange between vehicles and smart infrastructure, reducing congestion and improving safety.
Also Read:- Top IoT Communication Protocols [ ZigBee, NFC, and More ]
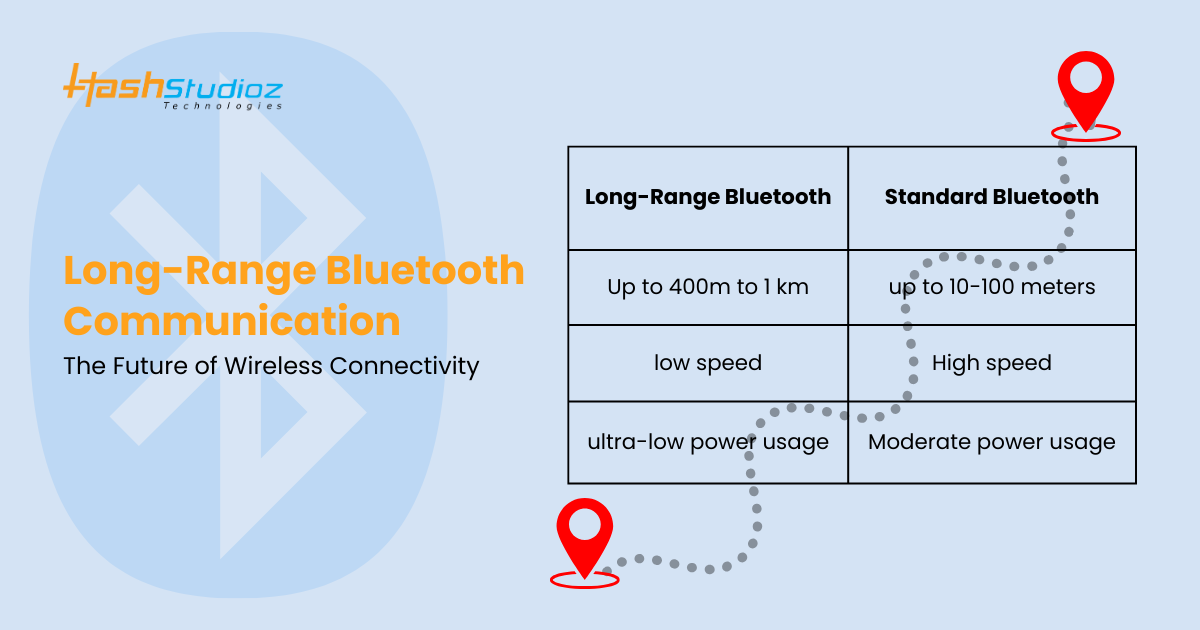
How Long-Range Bluetooth Devices Differ from Classic Bluetooth
| Feature | Long-Range Bluetooth | Classic Bluetooth |
| Communication Range | Up to 400 meters (open space) or 1 km (with optimal conditions using Coded PHY). | Typically 10–100 meters depending on power class. |
| Power Consumption | Low power: Designed for IoT and battery-operated devices. | Higher power: Consumes more energy for continuous data transfer. |
| Data Rate | Reduced for long range: Up to 125 kbps in Coded PHY mode for extended range; up to 2 Mbps for other BLE modes. | High data rate: Supports up to 3 Mbps for audio streaming and file transfers. |
| Use Cases | IoT devices, smart homes, industrial sensors, and medical monitoring over large areas. | Audio streaming (e.g., headphones, speakers), file transfer, and classic device-to-device connections. |
| Technology Base | Uses Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) with Coded PHY (S=2 or S=8) for extended range and robustness. | Uses Classic Bluetooth protocol without the range-extending features of BLE. |
| Energy Efficiency | Highly efficient; designed for intermittent data transmission and long battery life. | Less efficient; requires continuous power for streaming and higher throughput. |
| Connection Density | Supports many simultaneous connections (ideal for IoT environments). | Limited simultaneous connections; typically supports 7 active devices per master. |
| Latency | Optimized for low-latency communication, especially in BLE 5.2 and 5.3. | Higher latency, but sufficient for audio and file-sharing applications. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to smaller, simpler chip designs. | Higher cost for devices requiring higher data throughput and advanced audio codecs. |
When to Choose Long-Range Bluetooth Over Classic Bluetooth?
- For IoT Applications: Long-range Bluetooth is better for scenarios like industrial sensor networks, asset tracking, and remote environmental monitoring.
- For Low Power Needs: It’s the ideal choice for battery-operated devices like wearables, smart sensors, and medical devices.
- For Extended Coverage: Use cases like large smart homes, agriculture, or warehouse management benefit from its extended range.
Why HashStudioz? Because We Turn Complex IIoT Challenges Into Simple Solutions
Let HashStudioz simplify and accelerate your IIoT journey with powerful, easy-to-integrate solutions that improve your bottom line.