India is the world’s second-largest manufacturer of agricultural products, with agriculture employing nearly half of the country’s population. A sector that has such a large effect on the economy, simply relying on climatic conditions and manual farming practices, seems to be a little obsolete, and with the growing global population, a change in the system is more important than ever. This is why we believe that, with the advent of the smart Agriculture Sector, the Internet of Things sensor systems in agriculture can be used more commonly.
By health and fitness, home security, automotive, and smart cities, the Internet of Things (IoT) is increasingly entering our lives. As a result, it is clear that the Internet of Things, or connected devices, can be widely used in agriculture, enhancing its operations in any way. Since self-driving vehicles and augmented reality are no longer science fiction, the industry can no longer focus on animals or hand harvester tools.
Farming has experienced many technological transformations in the last decade or two, which is why it has become more developed and technology-driven. Farmers have greater leverage over the method of planting seeds and growing crops thanks to the use of smart farming devices. We were able to improve consistency and predictability by using this method.
Increasing demand for agricultural goods has resulted in a growth in the use of smart farming technology all over the world. Agriculture’s IoT market share hit $5.6 billion in 2021, and Internet of Things (IoT) application production is becoming more mainstream.
In this post, we’ll look at the Internet of Things (IoT) applications in the agriculture sector and their benefits. So, if you’re thinking about investing in smart farming or developing an IoT approach for agriculture, go for it.
Application of IoT in agriculture by segment 2020-2026
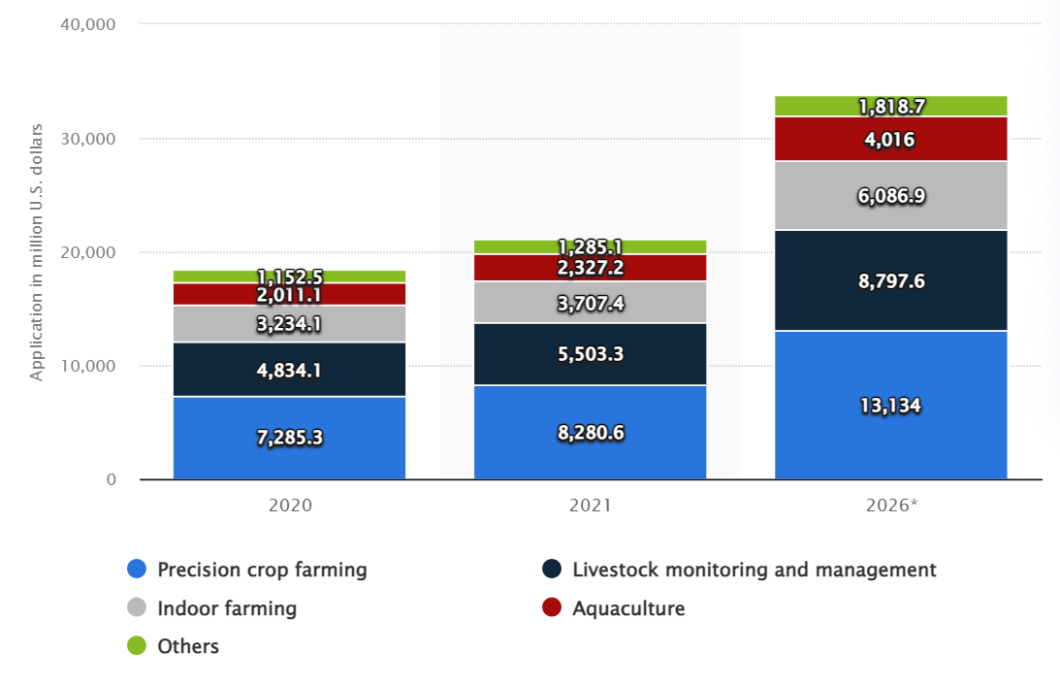
Table of Contents
What is Smart Farming?
The modern agriculture sector can be defined in a variety of ways. AgriTech, for example, refers to the use of technology in agriculture in general.
On the other hand, smart agriculture refers to the use of Internet of Things (IoT) solutions in agriculture. So, what does IoT-enabled smart agriculture entail? Farmers can make better decisions and develop just about any area of their job, from cattle to crop farming, by using IoT sensors to capture environmental and machine measurements.
Farmers, for example, can determine precisely how many pesticides and fertilizers they need to use by using smart agriculture sensors to track the condition of their crops. The concept of smart farming is the same.
The Role of IoT in Farming & Agriculture
About the fact that smart agriculture and industrial IoT aren’t as common as consumer-connected devices, the industry is still growing. The use of IoT solutions in agriculture is increasing steadily. According to BI Intelligence, the number of agriculture IoT system installs will reach 75 million by 2020, increasing at a rate of 20% per year. Simultaneously, the global smart agriculture sector is projected to triple in size by 2025, hitting $15.3 billion (up from slightly more than $5 billion in 2016).
Since the demand is still growing, there are still plenty of options for businesses that want to get involved. Building IoT agricultural goods in the coming years will help you stand out as an early adopter and pave the path to prosperity.
Why are we using the Internet of Things (IoT) sensor system in the first place?
Data on environmental conditions and the health of cattle and crops can be kept in one convenient location. Farmers will also examine and analyze the data to make sound decisions and anticipate future events.
A farmer, for example, might mount a sensor on a tractor or other piece of equipment. The sensor gathers data over time and sends an alert when a component is about to fail, allowing farmers to avoid costly downtime. To put it another way, IoT provides farmers with the visibility they previously lacked.
Internet of Things technology can be used in a variety of ways, depending on the needs of a specific region. Environment surveillance, greenhouse automation, seed monitoring, drones, and livestock GPS tracking are only a few examples.
Monitoring Climate Conditions

Weather stations with smart sensors can gather data on weather conditions and transmit it to farmers. This data will then be analyzed using special tools, giving the farmer a precise forecast that will help him prevent crop losses.
Crop Monitoring
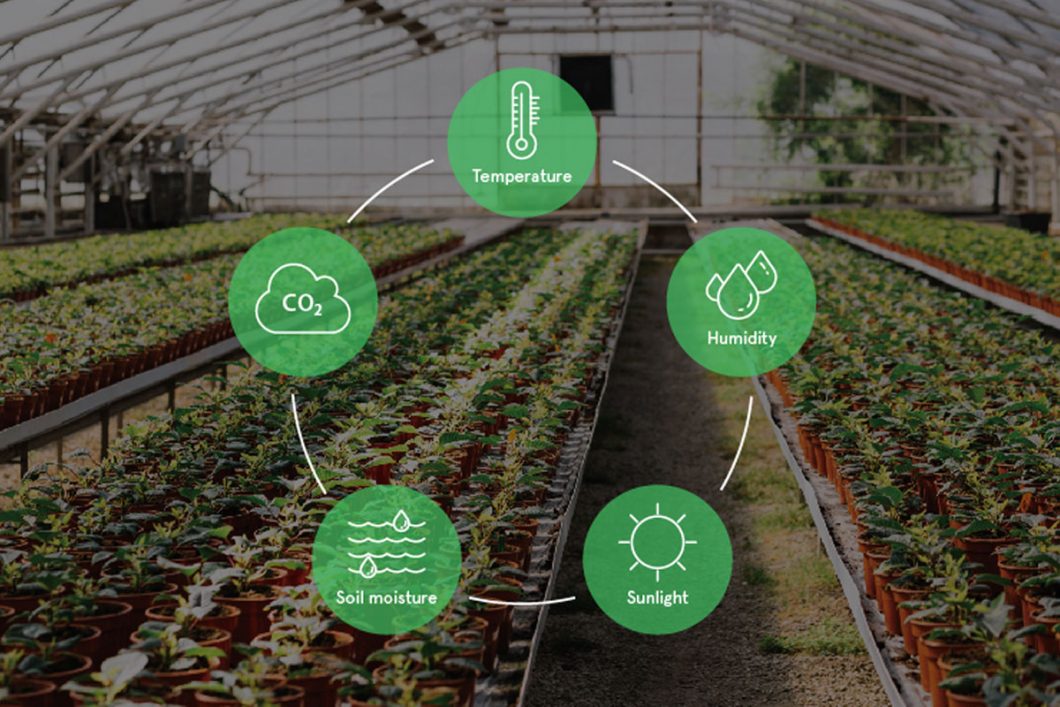

Sensors for crop tracking gather a wealth of data on crop health, humidity, precipitation, temperature, and other parameters, just as climate sensors do. Farmers who have access to this data can see any anomalies right away and take corrective measures. Farmers may also use sensors to decide the right time to grow and harvest crops.
One of the most well-known brands of farming machinery, John Deere, is one of the companies that has started to link its tractors to the Internet. They were able to view data about farmers’ crop yields using this tool.
Livestock GPS Tracking
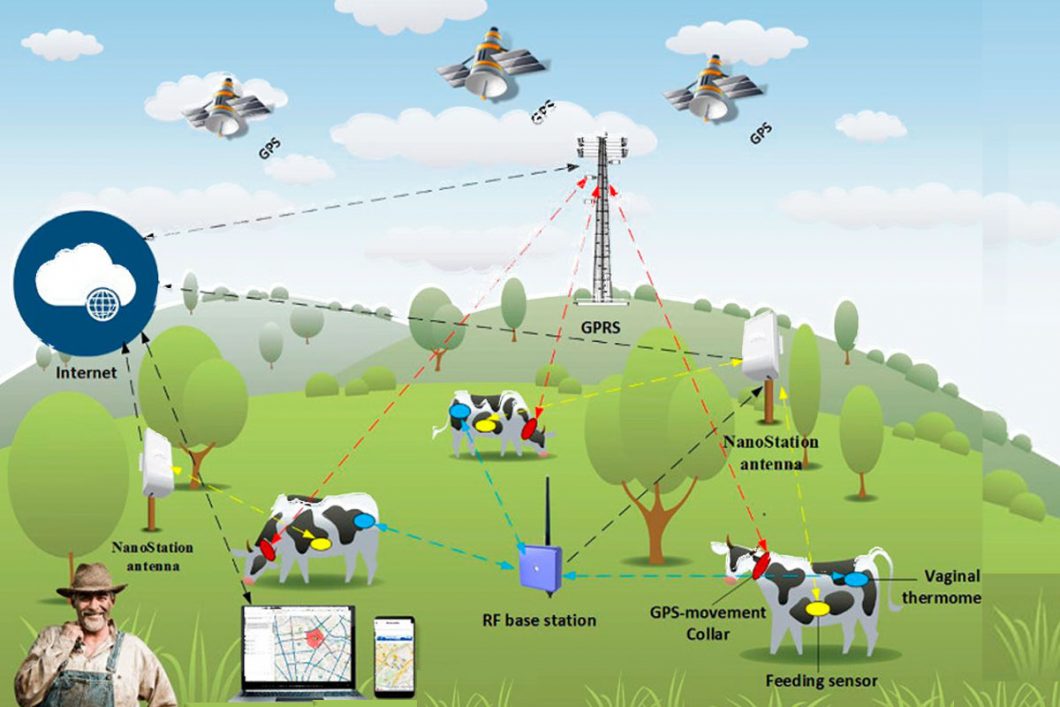
The use of IoT in livestock GPS monitoring has helped to revolutionize the farming industry by providing farmers with 24/7 remote, real-time visibility of their livestock.
Cattle cuffs with smart tags send out a signal every 15 minutes, enabling farmers to monitor their cattle’s position at any time and from anywhere. The signal is sent directly to a dashboard for livestock management. Farmers will use this dashboard to set up special presence detection and alerts that will alert them if their livestock leaves a specified location.
Cattle cuffs are particularly useful when it comes to livestock robbery, which is still the third most expensive crime in the UK farming industry. This type of crime not only causes untold cruelty to livestock as well as financial loss but also causes fear for farmers who have spent years building up their herds. Many cattle farmers manage vast herds, which means they can only spot lost cows after several days have passed. When profit margins are tight, finding out about lost cattle too late can be financially catastrophic.
IoT agriculture sensors may be used to track farm animals’ health and record results, similar to crop tracking. Livestock recording and surveillance aid in the collection of information about the health, well-being, and physical location of livestock.
Sensors to Measure Soil Properties
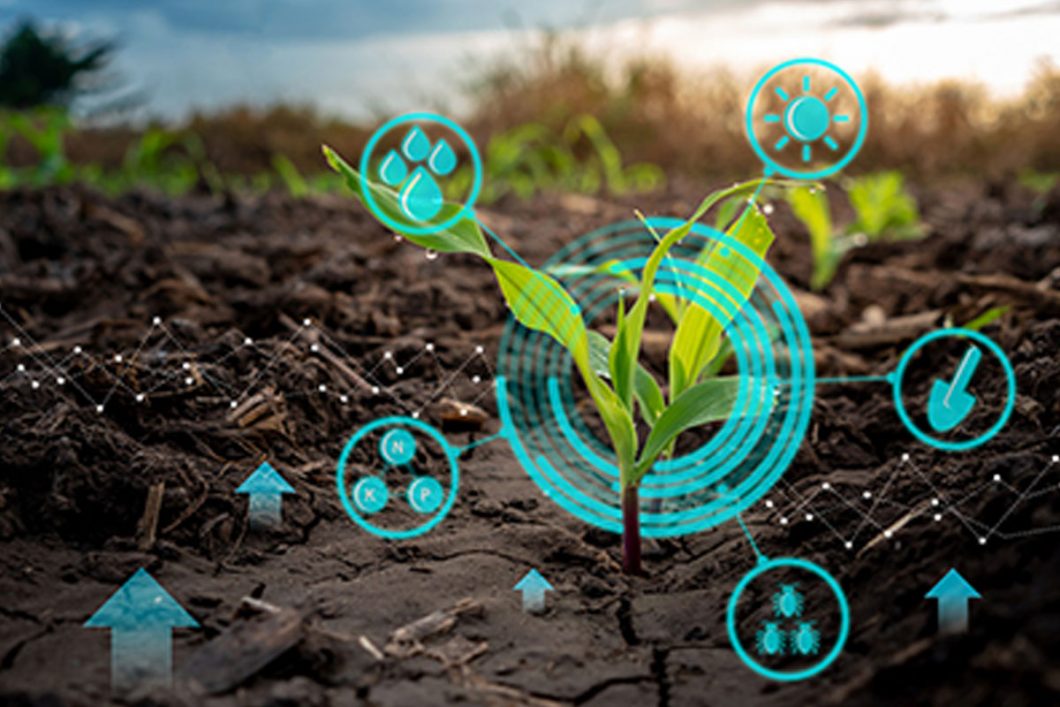

Optical Sensors- These sensors use light to quantify soil properties and were created to figure out how much clay, organic matter, and moisture there is in the soil.
Electrochemical Sensors– These sensors can detect the presence of O2, CO2, and other essential gases, as well as pH and soil nutrient levels. Relevant ions in the soil are detected by sensor electrodes that penetrate the soil. Determining essential nutrients can help crops thrive under the best conditions possible.
Dielectric Sensors- The moisture content of the soil is measured by these sensors. Once we know the moisture content of the soil, we can help irrigate the crops. Better water treatment results as a result of this. The pH of the soil can also be determined by using dielectric sensors.
End-to-End Farm Management Systems
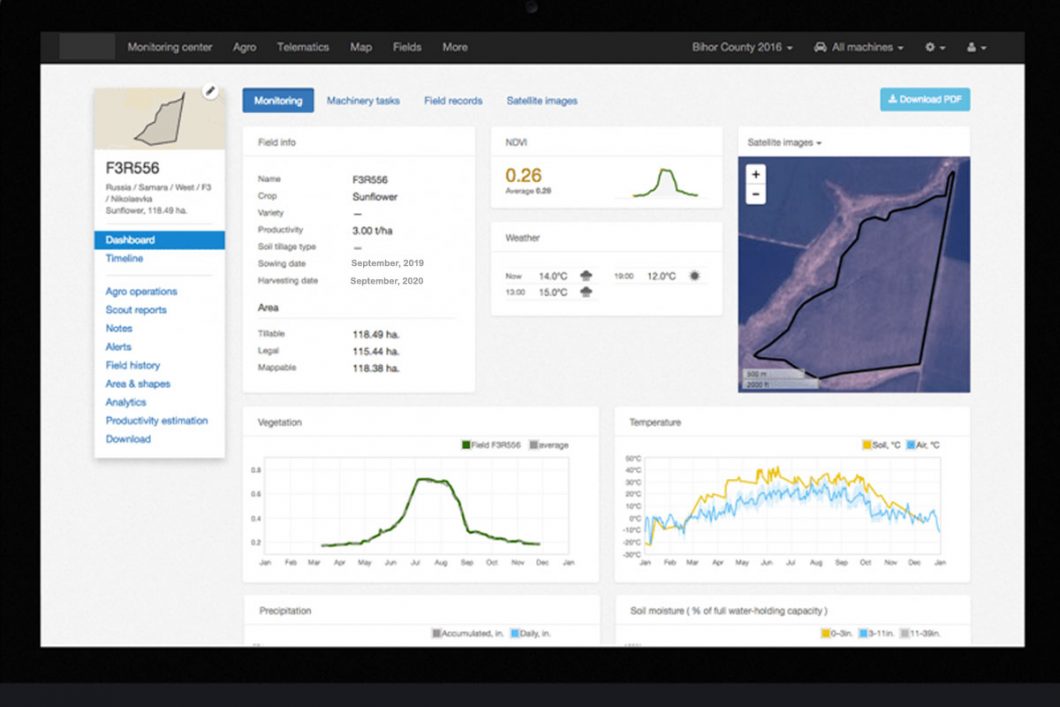
Farm productivity control systems are an example of a more complex approach to IoT goods in agriculture. They often comprise several on-premises farm IoT devices and sensors, as well as a sophisticated dashboard with analytical capabilities and built-in accounting/reporting tools.
This helps you to track your farm from away and streamline much of your business activities. FarmLogs and Cropio all provide similar solutions.
Vehicle monitoring (or automation), storage control, logistics, and other popular IoT agriculture use cases are only a few examples.
The Benefits of Smart Farming
Many aspects of the agriculture sector will benefit from new technologies and the Internet of Things. We’ll look at five aspects that IoT will help you improve:
- Climate conditions, soil quality, crop growth development, and cattle health are only a few examples. Data analysis will assist you in monitoring the condition of your business, as well as employee performance, equipment quality, and other factors.
- You will be able to help schedule the sale of your products once you know what your production output is. You will ensure the crops will not spoil or go unsold by having a precise understanding of crop location.
- The technology will detect seed damage early in the process, lowering the chance of yield failure.
- Smart devices can automate processes like irrigation, fertilization, and pest control in your development cycle.
- Automation enables the company to further track the production process, achieve higher crop quality levels, and expand its profitable capacity.
Finally, we’d like to find out that, while technology has helped many sectors in India, it’s past time for the agriculture sector to take advantage as well, thanks to sensor systems and smart farming.
Implementing IoT in the agriculture sector will have a huge impact. If you are looking to create an IoT Development Company solution for your agriculture business, our app experts at Contact Us are ready to help you create the ideal solution and get started. Also, You can reach at info@hashstudio.com

